Money and Credit Class 10 Notes:-
Table of Content:
Introduction to Money and Credit Class 10 notes :
We all have different needs and wants. Food, clothes, shelter, education, entertainment, etc. are the common things that everyone needs in their life. But all these are not freely available in the market. We all pay some amount of MONEY in return of such things.
Read this full article about Money and Credit class 10 Notes. It will be very helpful for class 10th students for notes of Chapter – Money and Credit. Let’s begin!
Understanding the process of Exchange :-
In this world every people haven’t have everything. Suppose, someone has ability to make shoes but someone is better in farming. The person who can make good shoes can’t live his whole life with shoes only, he will need many other things like wheat & grains and other food, clothes to wear etc. The person who is good in farming also needs other things, like clothes & shoes, shelter, education for his child, etc.
From here we can clearly understand that there is need of ‘exchange’ among people in the economy. The farmer could sell wheat to the shoe manufacturer and in return he could buy the shoes. And like this many other people can complete the needs of each other. In fact it’s in nature. We all exchange Carbon Dioxide, with Oxygen and food, from plants.
So it should be clear that ‘exchange’ is very important in the economy.
How goods were bought and sold when there was no money (Barter System)?
Earlier there was no money but it doesn’t mean that everything was free! Let’s understand how people use to exchange goods and services when there was no money…
Taking the example of shoe manufacturer, imagine he wants to sell his shoes in market and buy wheat but there is no such thing like money! So he has to directly exchange it with wheat. He would have to search for farmer who grows wheat and who wants to buy the shoes in exchange. Means both parties have to agree to exchange each other commodities. This is called double coincidence of wants. And this system of exchanging goods with goods is known as barter system.
Double coincidence of wants was very essential feature at that time. Without it people could not exchange their commodities.
Concept of MONEY :-
Looking for the person who is willing to exchange the commodity that you have with the commodity you want, was really a difficult task. To eliminate such limitations the concept of money was introduced.
Actually no one knows from where and who introduced the money. It is believed that in around 600 BC Lidiya’s king Alyattes introduced the first official currency, “The Lydian Stater”. The coins were made with a metal called ‘electrum’ which is the mixture of silver and gold that occurs naturally and they were stamped with pictures.
What is Money?

Money is a commonly acceptable instrument that people use to buy and sell commodities. It acts as an intermediate in the process of exchange and so it is called as “medium of exchange”.
It eliminates the need of double coincidence of wants. It is no longer necessary for a shoe manufacturer to look for a farmer who will buy his shoes and sell him wheat. All he has to do is find a buyer for his shoes. Once he exchange shoes for money, he can purchase wheat or anything in the market, with the money he has!
Modern forms of Money
As explained above, money is used as medium of exchange. It can be used in diferent forms. In early days grains and other commodities was used as the form of money . Afterwards, gold, silver, and other kinds of coins were used as money.
Now a days, people use money in various forms. Paper Notes, Coins, Cheques, etc. are use as forms of money. Widely, the modern forms of money includes: ● Currency ● Bank Deposits
Currency:
Currency includes all the paper notes and coins that are authorised by the government of the country. Previously the currency were made up of precious metals like gold, silver, etc. But now, cheap materials are used to make crrencies.
In India, Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the government of India. Different country use different names for their currency. The Indian law legalises “Rupees (₹)” as currency of India.
Bank Deposits:
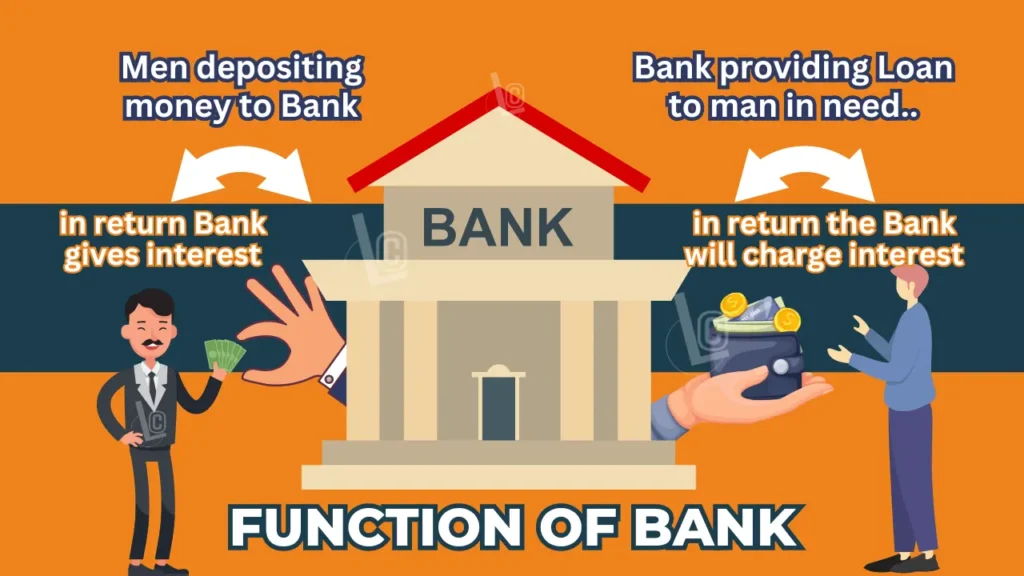
Bank deposits is the other form in which people hold money as deposits in bank. After all the necessary expenses, some amount of cash is left with the people. They deposit that extra part of currency in the bank with a motive to save it for future. In return, they get a fixed rate of interest from the bank.
The amount of money that they deposit in the bank can be withdrawn any time whenever they demand for it. That is why it is also called as demand deposits. This deposits offers one more good facility, that is payment through cheque.
Payment through Cheque:

A cheque is a paper that instruct the bank to pay a specific amount from the player’s account to the person to whom the cheque is issued. Basically the cheque is used to pay the amount directly from the bank account. It help to settle the payment directly from the account without taking the use of cash.
If you want to know more about Cheque and its uses then check out: Cheque and Types of Cheque
Loan Activity of Bank :-
Bank uses the amount, deposited by public who have extra money, to provide loans to the public who needs money. Major part of public deposits are used to provide loans. Bank charges some interest for the amount of loan that they provide. The difference between the internet they pay to depositors and the interest they charge to borrowers is the main source of income for the banks.
Two different Credit Situations :-
An agreement in which lender/supplier supplies money/goods/services to the borrower where the borrower promises to pay the amount in future. Two different credit situation is explained with the help of following examples:
Situation 1: Festive Season :
Salim, the shoe manufacturer, has received an order from large trader before two months of festival. To complete the order on time, he needed a few more workers and has to purchase raw materials. To meet these expenses, he obtained credit from two sources.
First, Salim asked the raw material supplier to supply goods and promises him to pay later. Second, he took some cash (as loan) in advance from the large trader and promises him to deliver whole order by the month.
At the end, he was able to deliver the order and he made a good profit. He repaid all the due amount that he had borrowed.
Situation 2: Swapna’s Problem :
Swapna, a small farmer, grows groundnut on her three acres of land. To meet the experiences of cultivation, she takes loan from the moneylender, hoping that there would be good harvest enough to pay back loan.
But by the end the crop fails and she is unable to repay the debt. Next year she takes fresh loan but the earnings are not enough to repay the loan amount. By the end she has to sell a part of her land to pay off the debts.
Situation 1 Vs Situation 2 :
In situation 1, Salim took the loan to meet the cost of production of goods. Cedit helps him to complete production on time. Credit here plays a positive role.
But in situation 2, Swapna took loan for farming purpose. But the results were not in her favour. The failure of crops made the repayment of loan impossible. As a result, she has to sell a part of her land. In this situation, credit creates a situation for the borrower from which recovery is very painful.
Terms of Credit :-
During the repayment of the loan amount, every borrower has to pay an extra amount that is he has to pay interest along with the principal amount he has taken. Before providing loans, the lender may demands ‘collateral’ (security) against loans. Collateral means the asset that the borrower owns. For example land, building, vehicle, etc. In case, the borrower is unable to repay the amount of loan with interest, the lender has right to sell the asset (collateral) of borrower to recover the loan amount.
Interest rate, collateral, documentation requirements, mode of repayment, etc collectively known as the Terms of Credit.
Formal Sector of Credit in India:-
People obtain loan mainly from the following sources:
▪️ Formal Sector
▪️ Informal Sector
- Formal Sector includes the loans obtained from banks, financial institutions, etc.
- The Informal Sector includes moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc.
- To control the loan activities of formal sector and to make sure that they would not only provide loans to rich business but also to small borrowers at balanced rate of interest, RBI supervises over the formal sector.
- But there is no any organisation which controls the credit activities of informal sector. They charge whatever rate of interest they want.
Formal and Informal Credit :
- From poor to rich, people are divided in various groups.
- Rich and Medium group people can easily get credits from formal sector. But for poors and rural peoples, getting loan from formal sector is very difficult.
- Formal sector meets only about half of the total loan needed by rural people.
- The poor and rural people therefor choose to get the loan from informal sector (moneylenders). They charge higher rate of interest as compared to formal sectors.
Cheap and affordable credit is very important for the growth of country. Therefore it is necessary for formal sectors that they have to increase lendings in rural areas, so that the people would not depend on informal sector.
Special Help Group (SHGs) :-
Rural people still could not get loans from formal sector as:
▪️ The banks are not available everywhere in villages.
▪️ If banks are available then also it is very difficult process to obtain loans from them.
To overcome from this problem people tried a new way and formed Special Help Group (SHG). SHG is basically a small group of rural people who meet and promote small savings. Group contains typically 15-20 people basically of neighbourhood.
Advantages of SHG:
- Promotes small savings among the people in group.
- Helps to provide loans at cheaper rate of interest than the moneylenders.
- Building blocks of organisation of the rural people.
- Help women to be self dependent.
- Regular meetings of people helps to discuss on the various problems and get solution for the same.
Hope this post help you for your class 10th Economics notes for chapter – Money and Credit. 🙂
Follow our IG Page for Commerce – @Commerce_Craze
FAQs
- What is money?
Ans – Money is Commanly acceptable instrument that is used to exchange goods and services. - How many currencies are there in the World?
Ans – There are 180 currencies in the World. - How many sectors of Credit are there in India?
Ans – There are mainly two sectors of Credit in India. Formal Sector and Informal sector. - How a Bank earn their profit?
Ans – Banks earns profit by providing loans at higher rate. It gives interest to depositors and charges interest from borrowers. The difference between the amount of interest given and charged is its profit.
