Forms of Business Organization: Class 11th Notes
If you have decided to open and run your own business, then you must decide that which forms of business organization you have to open. This decision is based on various things, like – capital you want to invest, number of people needed, business size, etc. Understanding the various forms of business organization is also important for students of Class 11th Commerce. From sole proprietorship to joint stock companies, each form comes with distinct features, merits, and demerits. This article aims to clarify these aspects, providing a comprehensive guide for Class 11 Commerce students.
Importance for Class 11th Commerce Students:
Students who have choosen commerce as their field, need a solid knowledge of these forms of business organization to understand the complexity of the business world. This knowledge lays the foundation for their future undertakings in the field.
Table of Content:
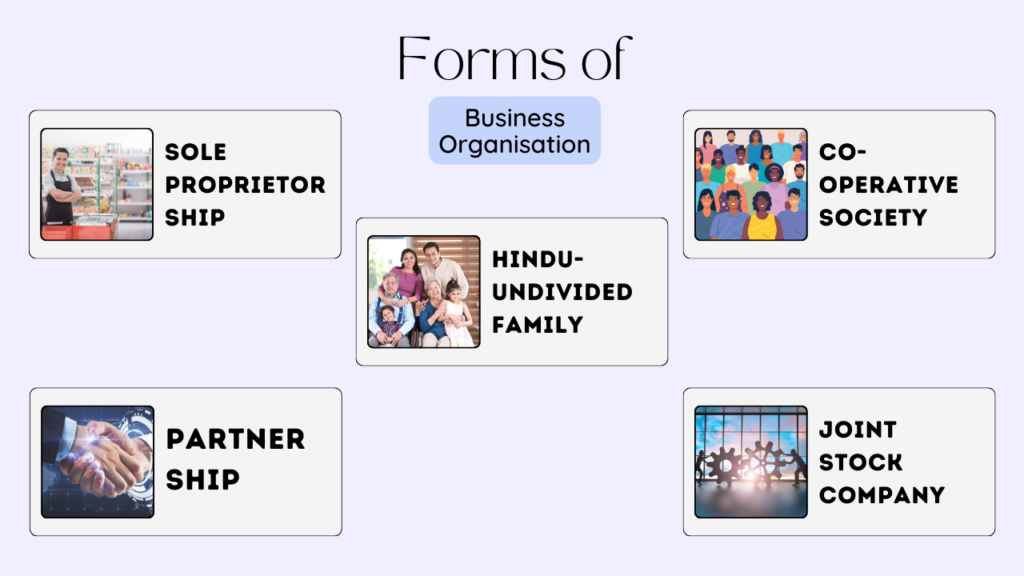
Various Forms of Business Organization includes:
I. Sole Proprietorship
II. Joint Hindu Family Business
III. Partnership Firm
IV. Cooperative Society
V. Joint Stock Company
I. Sole Proprietorship:
Sole proprietorship is the simplest forms of business organization where a single individual owns and manages the business. The word “sole” means “single”, and “proprietor” means “owner”. So, a sole proprietor is the single person who is the only owner of a business. This form of business mainly includes commonly operated shops like General Stores, Sweets Store, Beauty Parlours, Saloons, etc.
Features of Sole Proprietorship:
- Single Ownership: Owned and operated by a single individual.
- Simple to Start: Easy and inexpensive to set up.
- Direct Control: The owner has full control and decision-making authority.
- Sole Profits: All profits belong to the owner.
- Tax Benefits: Business income is taxed as the owner’s personal income.
Merits:
- Easy decision-making.
- Direct control by the owner.
- Confidentiality of information.
- Easy to form and close.
Demerits:
- Limited resources.
- Unlimited liability for the owner.
- Limited managerial ability.
II. Joint Hindu Undivided Family Meaning (HUF):
HUF is a unique in all forms of business organization where business organisation found only in India. It is run by a family, and ownership passes down generations. It is one of the oldest form of business in India. It refers to a form of organisation in which the business is owned by the members of the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). It is governed by Hindu Law.
The business is controlled by the head of the family who is the eldest person in family and is called as ‘KARTA’. All the member of family have equal right over the property and they are known as co-parceners.
Features of HUF:
- Minimum two members are needed in the family.
- Governed by Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
- Liabilities of Karta is unlimited, but liabilities of other members are limited to their shares.
- All the control of the business is lies with the Karta.
- Inclusion of new members occurs at the time of birth in HUF.
Merits:
- Business continues to run even after death of Karta.
- Limited liabilities of members.
- There is greater sense of loyalty and understandability towards each other. As the members are family.
Demerits:
- Limited resources and capital.
- Unlimited liability of Karta.
- Limed managerial skills.
III. Partnership
This forms of business organization involves two or more individuals sharing ownership. According to Section 4 of The Partnership Act, 1932, “The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”
This definition explains the essential elements of a partnership, which include mutual agreement, the intention to share profits, joint business activities, and collective responsibility among the partners. In a partnership, individuals join together to engage in a common business venture, with the understanding that they will collaborate in both decision-making and the distribution of profits arising from the business activities.
Features of Partnership:
- Minimum two persons needed.
- Sharing of responsibility and control among partners.
- Mutual Agency.
- Long-term Continuity.
- Risk bearing by all Partners.
Merits:
- Diverse skills and expertise.
- Shared financial burden and risk.
- More funds collection.
- Ease of formation and closure.
- Balanced decision making.
Demerits:
- Limited resources.
- Unlimited liability.
- Possibilities of conflicts among partners.
- Lack of continuity.
IV. Cooperative Society
Cooperative societies involve individuals working together with a common objective. It is voluntary association of persons, who join together with the motive of welfare of the members. They are motivated to protect their economic interests, from the exploitation of middlemen (who are obsessed with the desire to earn greater profits).
The cooperative society is compulsorily required to be registered under the Cooperative Societies Act 1912. The process of setting up a cooperative society is very simple. This required only the consent of at least ten adult persons to form a society. The capital of a society is raised from its members through issue of shares. The society has a distinct legal identity after its registration.
Features of Cooperative Society:
- Voluntary Association: A person is free to join a cooperative society and can also leave anytime.
- It has separate legal status and registration of it compulsory.
- Members of cooperative society have limited liability to the extent of the amount of share they contributed.
- Control is in the hand of an elected managing committee.
Merits:
- Equality in voting status.
- Limited liability of the members.
- Runs continually, its existence is not affected by its members.
- It has support from the govt. in the form of low taxes, subsidies, etc.
- Easy formation.
Demerits:
- Limited capital.
- Inefficient management system.
- Lack of secrecy.
V. Joint Stock Company
A company is an association of persons formed for carrying out business activities and has a separate legal status independent of its members. A company can be described as an artificial person having a separate legal entity, perpetual succession, and a common seal.
It is governed by The Companies Act, 2013. As per Section 2(20) of Companies Act, 2013, “A company means a company incorporated under this Act or any other previous company law.”
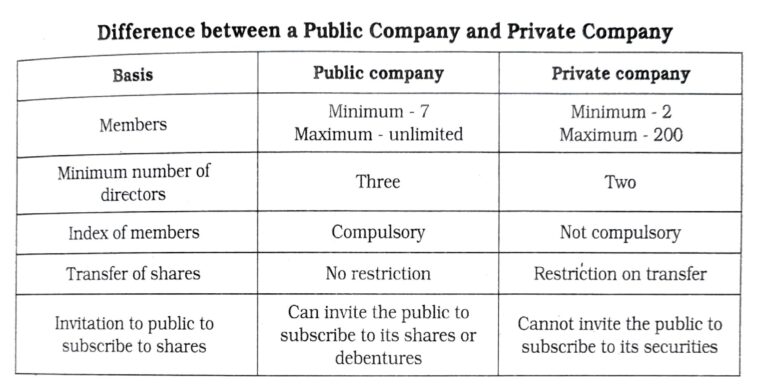
The shareholders are the owners of the company, and the Board of Directors is the chief managing body elected by the shareholders. The capital of the company is divided into smaller parts called ‘shares’ which can be transferred freely from one shareholder to another person (except in a private company).
Features of Joint Stock Companies:
- Separate legal entity.
- Artificial Person.
- Formation includes several complicated processes.
- Perpetual Succession – It can be opened and end only by law.
- Control is with the Board of Directors, selected by shareholders.
- Liability of shareholders is limited to the extent of the capital they invested.
Merits:
- Limited liability of the members.
- Shareholders can easily convert their investment to cash by selling their share in the market.
- Large source of financial resources provide better scope of expansion.
- Better management with professionals and specialists.
Demerits:
- Complex information system.
- Lack of secrecy. Means all the information are shared to public time to time.
- Many regulations and legal compulsions.
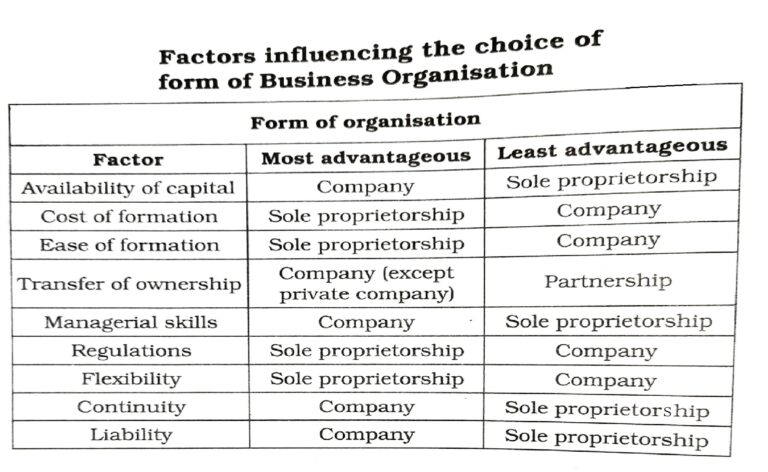
How to choose? (Factors influencing choice of Forms of Business Organisations)
On the basis of following points, one can decide that which forms of business organization he/she has to open.
- Cost and Ease of setting up the Business.
- Management Ability to run the Business.
- Capital you have to invest.
You can also checkout this topic on Forms of Business Organization in short and easy words on our instagram post on Page – @Commerce_Craze. Link – Click Here
